Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
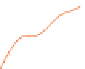
Fig. 3.1
ANN classification accuracy in relation to the number of considered features, observed in
sequential backward elimination process while employing feature ranking obtained by Relief filter:
a
decreasing order,
b
increasing order. For each median there is indicated maximal and minimal
performance
We can observe that reduction of the highest ranking features in the initial phase,
for just few variables discarded, gives a slight increase in performance, but it soon
falls down to an unacceptably low level. On the other hand, rejection of low ranking
features enables to keep the classification accuracy at sufficiently high level even
when there are only few inputs left for the network to learn from.
Similar results were obtained for rule classifiers as shown in Fig.
3.2
. The trends
reflect those previously detected, but overall comparison of both types of classifiers
indicates that ANN outperforms DRSA decision algorithm. This conclusion is not
entirely accurate due to the fact that the network with the used topology classifies
without any ambiguity while for DRSA classifier ambiguities did occur and were
treated as incorrect decisions.
Fig. 3.2
DRSA classification accuracy in relation to the number of considered features, observed
in sequential backward elimination process of all rules on examples algorithm, while employing
feature ranking obtained by Relief filter for a decreasing order (Most series), and increasing order
(Least series)























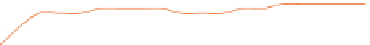




























































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search