Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10.4.4 Level Set Representation
In this section, we outline the level set representation for the region-aided geo-
metric snake. Level sets describe a moving front in an implicit function and are
the basis for the numerical algorithm for curve evolution according to functions
of curvature, introduced by Osher
et al.
[15, 16]. In the application to active con-
tours, the evolving contour is embedded into a higher dimensional surface as a
zero level set. The entire surface, the level sets, is an implicit representation of
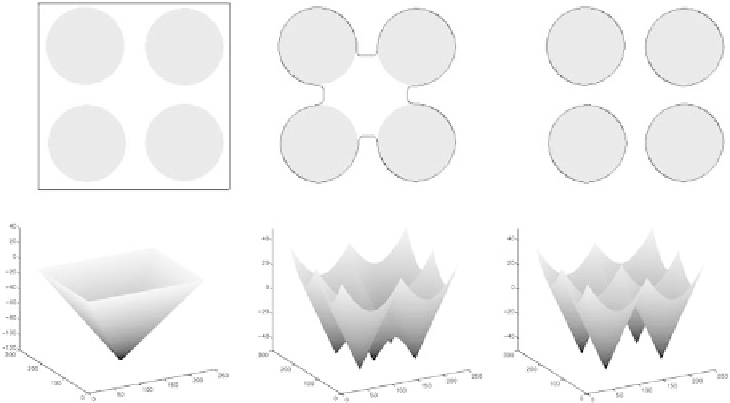
the embedded contour. As shown in Fig. 10.13, the snake is initially built in a
three-dimensional surface, which later evolves according to underlying forces.
Finally, the converged snake is extracted from the level sets by cutting it at zero
height.
Let
C
be a level set of a function of
φ
:[0
,
a
]
×
[0
,
b
]
→
. That is,
C
is
embedded into the zero level set with
φ
being an implicit representation of the
curve
C
. This representation is parameter free and intrinsic. Given a planar
curve that evolves according to
C
t
= F
N
for a given function
F
, the embedding
function should deform according to
φ
t
= F|∇
φ
|
, where
F
is computed on the
level sets. By embedding the evolution of
C
in that of
φ
, topological changes
Figure 10.13:
Level sets evolution for an embedded snake. Top row: initial
snake on test image, evolving contour, and final converged snake. Bottom row:
corresponding evolving level sets. The snake is tracked at zero height.