Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
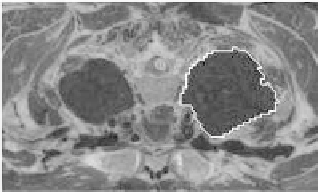
Figure 7.6:
Original image with the outlined initial contour.
The obtained contour was plotted over the original image for matching
(Fig. 7.6). If compared with Fig. 7.4(b) we observe an improvement in the ob-
tained initialization.
7.3.3 Neural Nets
Neural networks have been used for instantiating deformable models for face
detection [54] and handwritten digit recognition tasks [74] (see also [14] and
references therein). To the best of our knowledge, there are no references using
neural nets to initialize deformable models for medical images. However, the
network system proposed in [25], which segments MR images of the thorax,
may be closer to this proposal.
In this method each slice is a gray-level image composed of (256
×
256) pixels
values and is accompanied by a corresponding (target) image containing just
the outline of the region. Target images were obtained using a semiautomatic
technique based on a region growing algorithm. The general idea is to use a
multilayer perceptron (MLP), where each pixel of each slice is classified into a
contour-boundary and non-contour-boundary one.
The inputs to the MLP are intensity values of pixels from a (7
×
7) window
centered on the pixel to be classified. This window size was found to be the
smallest that enabled the contour boundary to be distinguished from the other
image's artifacts. The output is a single node trained to have an activation of
1.0 for an input window centered in the pixel of a contour boundary, and 0.0
otherwise. The network has a single hidden layer of 30 nodes.
The network was trained using error backpropagation [12, 55] with weight
elimination [72] to improve the network's generalization ability. The training
data should be constructed interactively: A proportion of misclassified exam-
ples should be added to the training set and used for retraining. The process