Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
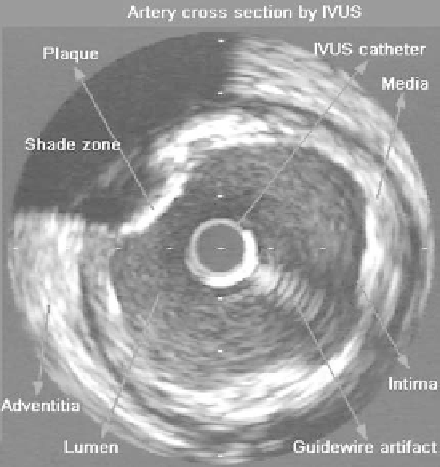
Figure 1.1:
Typical 2D IVUS image indicating the location of the principal mor-
phological arterial structures and artifacts.
place if the increase in stenosis persists and can become serious due to a throm-
bosis. The result can be an infarct. The introduction of intravascular ultrasound
(IVUS) [3, 4] in the field of medical image as an exploratory technique has made
a significant change to the understanding of thearterial diseases and individual
patterns of diseases in coronary arteries. Although coronary angiography [5, 6]
provides with 2D information about the coronary anatomy, serving as a guide
in operations, it has limitations when not allowed to access the mechanism of
the disease, its composition, and its extent. On the contrary, the IVUS tech-
nique shows the cross-section (Fig. 1.1) of the artery, allowing an evaluation
of the plaque as well as of the different layers in the arterial wall. The IVUS
image [2, 5, 6] provides qualitative (Fig. 1.2) information about the causes and
severity of the narrowing of the arterial lumen, distinguishes the thrombus of
the arteriosclerotic plaque, shows calcium deposits in the arterial wall, eval-
uates the changes and complications in the coronary arteries that occur after
an intervention such as angioplasty, evaluates and diagnoses coronary arterial
aneurysms, and diagnoses fissures of arterial coronary plaques: determination
and location, dimensions, type (eccentric and concentric), and composition of
the arteriosclerotic plaque.