Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
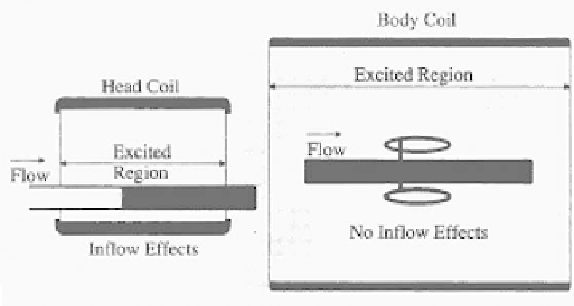
Figure 3.28:
Excitation in coil.
Since the 2D method is a multiple-single-slice technique, the slices are re-
constructed as they are collected. They may be viewed while subsequent slices
are being collected. This feature allows the operator to monitor the data collec-
tion. Later, data collection may be stopped to correct the protocol, if necessary,
without waiting for all the data to be collected. It also shortens the study time by
reconstructing the slices while the acquisition is still in progress. In our experi-
ence for routine transverse slices of the carotids, processing methods consist of
projecting the stack of slices in a plane orthogonal axis. Top-down projections
or perpendicular projections in the AP direction may be generated with appro-
priate selection of projections in the select procedure menu (see Fig. 3.28). First
projection will be generated when slices are reconstructed. INFLOW image pro-
cessing uses a maximum intensity projection with the interpolation between the
slices. The maximum intensity voxel in a given vector is used for that projection
view.
3.3.2 FLAG, RSE-Phase Contrast
Flow adjusted gradient (FLAG) and RSE are fast field echo sequences. They
have velocity-sensitive gradients that are designed to image flow by adjusting
their sensitivities to different flow velocities. The contrast between flowing and
stationary tissue is based on the phase of the transverse magnetization of moving
spins rather than on time-of-flight effects. Spins moving in the presence of a mag-
netic gradient accumulate a flow-induced phase shift. This phase shift depends
on the strength and duration of the gradient and the velocity of the moving spins.