Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
moves superiorly with each successive tissue slice. As a result, the image data
set emphasizes exclusively arterial structures.
3.2.1.3 2D TOF Angiography of the Carotid Bifurcations
In patients with vascular diseases, the 2D TOF imaging technique is an effective
method of imaging the carotid artery bifurcation. We acquired typically 50-70
contiguous axial slices, each approximately 1.5 mm thick. The acquisition is
performed by using flow compensation in both slice-select and read-out direc-
tions. For this, typically a gradient echo pulse sequence is employed, with TR
=
45-50 msec, a flip angle of 45-60
◦
, NEX
=
1, 128
×
256 matrix, and minimum
available echo time. The field of view (FOV) may vary from 16 to 20 cm, depend-
ing on the patient size. As a result, axial image slices show the blood vessels as
bright (see Fig. 3.8). Other surrounding tissues appear with much lower signal
intensity. However, the 2D TOF angiography method has limitations.
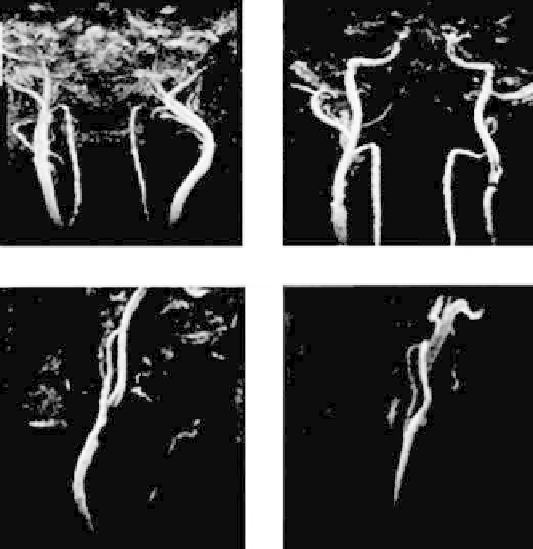
Figure 3.8:
In carotid artery, glomus tumor vasculature is shown in pre- and
postsurgery (left and right panels at the top). Carotid stenosis (left on bottom)
and carotid aneurysm (right at bottom) are highlighted.