Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
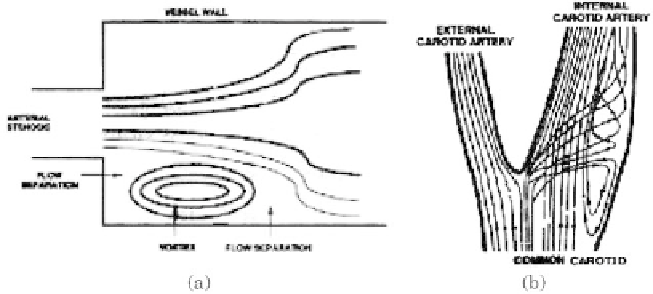
Figure 3.3: The central streamline flow separating from the vessel wall to pro-
duce a vertex or flow eddy stagnant blood to cause hemodynamic condition in
VMRI (on left). The flow pattern at carotid bifurcation shows countercurrent
flow and flow separation phenomena within the carotid bifurcation.
flow is maximum. Turbulent flow is defined as a rectangular flow pattern. The
flow velocity is high in the whole region and vortices do appear. Adjacent layers
are mixed. The flow is known as 'plug flow' otherwise velocity as a function of
spin position is defined by Laminar flow as following:
V
(
r
)
=
V
max
[1
−
(
r
/
a
)
2
]
(3.3)
where
a
is radius of vessel as cylinder. So, the plug flow for every phase-encoding
step may be defined at constant flow as:
ρ
(
x
,
y
)
=
e
i
γ
G
0
ν
(
x
,
y
)
τ/
2
.ρ
(
x
,
y
)
τ
(3.4)
where
G
0
is bipolar pulse strength and
τ
is length of time and phase is
γ
G
vτ
2
with flow along
x
. In case of velocity as function of spin position for the flow
along
x
when vessel is in-plane the laminar flow may be defined as:
ρ
(
x
,
y
)
=
e
i
γ
G
0
ν
(
x
,
y
)
τ/
2
.ρ
(
x
,
y
)
(3.5)
These flow characteristics are interrelated by Reynolds number,
Re
, as:
Re
=
2
R
0
v
a
v
ρ/η
(3.6)
where
ρ
is density and
η
is viscosity of fluid.
For
Re
>
2000, the flow is defined as turbulent flow. For
Re
>
7000, the flow
is defined as pulsatile flow as observed in arteries for a transition state between