Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(
p
)
[
p
]
E
M
/
E
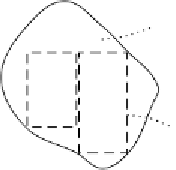
Figure 2
Equivalence classes, p
E
, induced by an observable , form a partition
M/E
. The values p in the range M act as
labels
to the equivalence classes.
1
M
1
[
M
]
M
/
E
1
×
≅
M
2
2
[
M
]
M
/
E
2
Analysis of
M
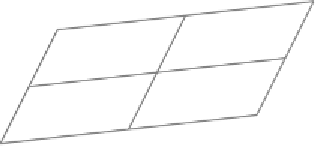
Figure 3
The analysis of a natural system, represented by M, leads to an analytical
model
a
M which describes M in terms of the direct product of image sets and
partitions induced by observables
i
.
As shown in Fig. 3, two observables can provide more information than one,
→
×
M
2
M
p
→
1
p
2
p
1
M
such that
1
M
×
2
M
M/E
1
2
where
E
1
2
=
E
1
∩
E
2
means that for any two values p and p
1
p
=
2
p
and
1
p
=
2
p
. That
is, the equivalence classes of E
1
2
are the intersections of all the equivalence