Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
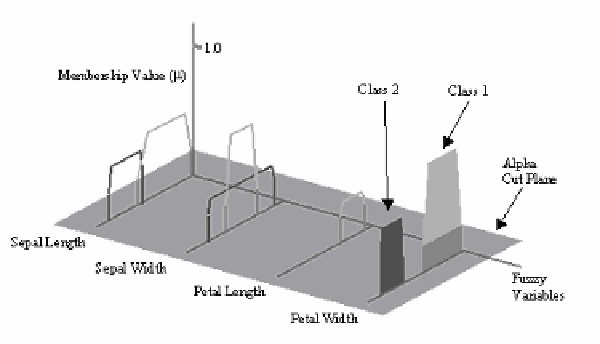
Fig. 9.
A 3D parallel plot of Iris data example [Pham & Brown, 2003].
Another improvement can be made by asking doctors to provide the as-
sessment of diagnostic categories with fuzzy grading. For example, instead of
Healthy, three grades are introduced: Very Healthy, Moderately Healthy, and
Slightly Healthy. Similarly, disease conditions can be expressed in three grades:
Very Serious, Moderately Serious, Slightly Serious. Such fuzzy assessment would
match more faithfully with real diagnosis practice. By linking fuzzy values for
the color and texture features of the tongue with fuzzy diagnostic categories, it
is envisaged that a more accurate classification of cases would result. However,
in order to achieve this, we will need to collect more cases and more detailed
diagnosis from doctors for each case.
7 Diagnosis with Neural Computing
Fuzzy visualization methods provide a promising interface for medical doctors to
interact with the ambient diagnostic systems, especially at the early explorative
stages. As we gain more insight about the data, it is time to build numerical
models for diagnosis.
Ambient diagnostics is made largely by the interconnected elements. The
metaphor can be simulated by artificial neural networks, which are composed of
simple elements operating in parallel. We can train a neural network to perform
a particular diagnostic function by adjusting the values of the connections (soup
of weights) between elements. In the supervised learning process, many such
input/target pairs are used to train a network [62].
Radial Basis Network is a feedforward backpropagation network. It is fast
but needs more neurons so requires more memory [63]. It is also simple to be
implemented on hardware, for example, a neural network on a chip, can perform
1 million recognitions per second. In a radial basis function network, each hidden
unit produces a ball-shape 'pulse' driven by a Gaussian function. The output unit
produces a linear combination of hidden unit pulses. In this case,
R
(
n
)=
e
−n
2
(11)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search