Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
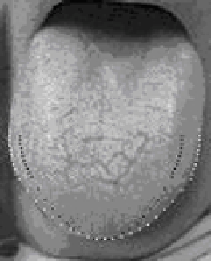
Fig. 4.
Cracks on the Tongue.
off thresholding for the rest of the image. Since an adaptive threshold considers
each block individually, this problem is avoided. For each window analyzed, the
adaptive threshold sets its threshold first by finding the mean value and standard
deviation of non-black pixels, and then setting a threshold based on these values.
This allows the thresholder to provide consistent behavior for images with dif-
ferent illuminations, provided they fit a relatively normal lighting distribution,
which was found to be typical for the tongues analyzed. For this project, the
mean pixel value was used.
The next part of step one is to invert the V channel. This is done to reflect
the fact that the cracks are dark in the V channel. By inverting it, the cracks
(which would have been thresholded down to 0) are once again changed back to
1. The next step, essentially an “AND” operation on both images, chooses all
pixels that appeared “bright” in the S channel and “dark” in the V channel.
At this stage, there is still a lot of noise. The main cracks, however, appear
to be large, whereas the noise is limited down to small size pixels. To remove the
noise in the image, the image is first eroded, then all remaining small pixels are
removed. Eroding is a morphological operation that shrinks objects in an image,
much like land erosion washes away dirt on hills, making the hills smaller. Erosion
works by passing a structuring element over the image, and outputting a pixel
only when the structuring element is completely covered by pixels in the original
image [49].
Once the image has been eroded to enhance the separation of objects in the
image, all objects belonging on the fringe edge of the image are removed. This is
done to prevent erroneous detection of cracks that are really just places on the
edge of the tongue where illumination falls off steeply. The first step in doing
this is to calculate a mask that describes the edge of the tongue by thresholding
the image. The mean pixel value of the non-black pixels in the image minus
one-half of the standard deviation of the non-black pixel values is used as the
threshold. Next, this mask is smoothed by performing a closing operation on it.
Closing is simply dilating the image then eroding it, and has the effect of closing
small gaps in the image. Just as dilating has its counterpart eroding, closing has
a counterpart called opening which does the opposite by eroding then dilating.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search