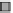Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CO
Nox
NH3
Direct
PM2.5
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
Percent of emissions
Stationary fuel combustion
Industrial and other processes
Highway vehicles
Nonroad mobile
Figure 10.1
Distribution of emissions in the United States by source category for specifi c pollutants,
2007. (Environmental Protection Agency)
incidence of eye infections has also risen. Babies born in areas where air
pollution is most severe have smaller lungs, lower birth weights, smaller
heads, damaged DNA, lower IQs, and increased rates of birth defects.
Women who live within a half-mile radius of areas of high emissions,
such as major roads or factories, are two to four times more likely to
give birth to children who develop cancer.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, children are more
vulnerable than adults to many airborne contaminants. The cellular
immaturity of children and the ongoing growth process account for this
elevated risk. Since children breathe more rapidly and even inhale more
pollutants per pound of body weight than do adults, even minor irrita-
tion caused by air pollution, which would produce only a slight response
in an adult, can result in a dangerous level of swelling in the lining of
a child's narrow airways. Increased exposure to air pollutants during
childhood increases the risk of long-term damage to a child's lungs.
Worldwide, respiratory disease is second only to polluted water as the
greatest killer of children. Air pollution causes elderly people to die
prematurely from heart attacks because their weakened lungs cannot
process enough oxygen. In New Delhi, 20 percent of the traffi c police at
busy intersections need regular medical attention for lung problems. Bus
drivers in urban areas in the United States have increased cancer rates,