Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
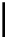
Fig. 2.8
Schematic map of accumulated and fixed energy-savings of 11th FYP. Note: the
accumulated energy-saving is the sum of square 2006 to square 2010,while fixed energy-savings
is the triangle of 2006 to 2010. The horization axis is the GDP and the vertical axis is referred as
energy intensity
2.2.1 Actual Performance of Energy Intensity
Since the energy intensity indicator is a function of energy consumption and the
GDP, whether the energy-intensity target for the 11th FYP was achieved depends
on GDP and energy consumption from the year before.
In early 2011, Beijing released the 2010 Statistics Bulletin of the National
Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China.
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) launched the
preliminary assessment of energy intensity and carbon emission indicators of the
11th FYP in March 2011 and the State Council issued the
Energy Conservation and
Emission Reduction Planning of 12th FYP
in August 2012.
Based on the official assessment on Energy-saving and Emission Reduction
Efforts during the 11th FYP, the energy intensity reduction amounts to 19.1 %
(see Fig.
2.9
); the accumulated energy savings exceeded 0.6 billion tce, which
amounts to 1.4 billion tons of CO
2
reductions.
As mentioned-above, the energy intensity was reduced by 19.06 % in 2010
compared with 2005 and the accumulated energy-savings was about 635 Mtce,
based on the latest data from the China Statistical Yearbook of 2012.
Looking at year-on-year energy intensity improvements based on the latest
information,
4
it can be found that the nation reversed its backward momentum of
energy intensity obviously in 2006, when it declined by 2.72 %; in the next 2 years,
4
China Energy Statistical Yearbook [
2
].