Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
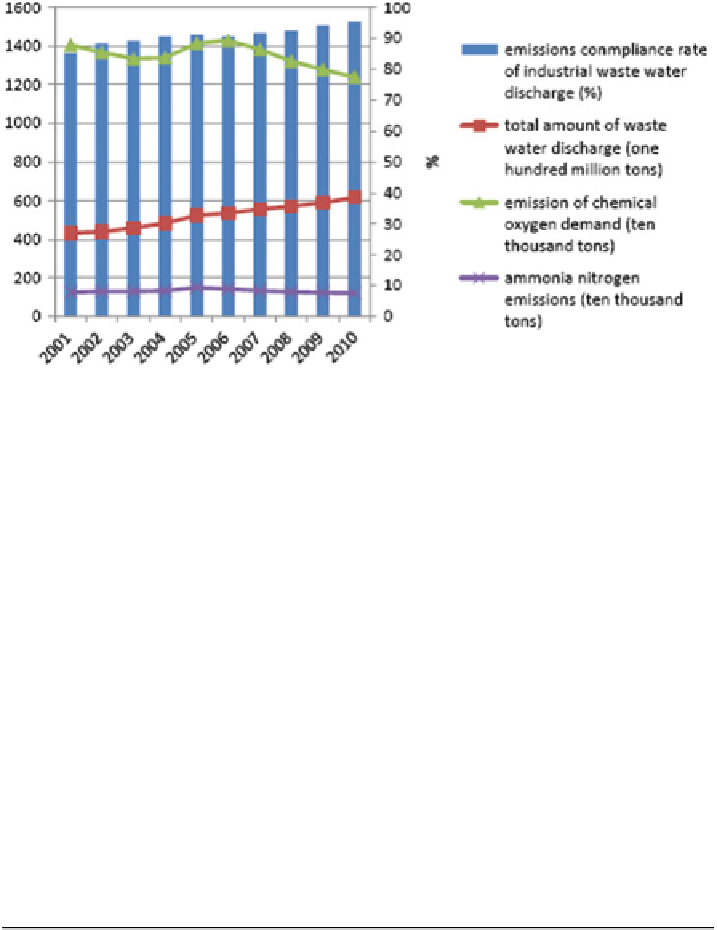
Fig. 6.2
National waste water and its compliance rate (Source: National Bureau of Statistics,
China Environment Statistical Yearbook 2011
)
of cities that suffered from heavy acid rain (precipitation PH 4.5) was almost the
same as that in 2009. China's regions that are most affected are mainly distributed
throughout the region south of the Yangtze River and to the east of the Tibetan
Plateau region, including most areas of Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Hunan, Fujian,
Chongqing and the Yangtze River Delta region. The area of land affected by acid
rain covers about 1.2 million square kilometers, and the area affected by heavy acid
rain covers about 601,000 km
2
.
Air pollution prevention still has a long way to go. China's coal-based energy
structure has not fundamentally changed. Coal and smoke pollutants remain the
main forms of pollution, and urban air quality issues, such as sulfur dioxide and
PM10 pollution, have not been fully resolved [
7
]. Meanwhile, the amount of motor
vehicles on the road continues to rise (As of November 21, 2010, the number of
cars in Beijing totaled 4.67 millions), pollution from exhaust has seen a dramatic
increase and compound atmospheric problems, such as gray haze, photochemical
smoke and acid rain, have become prominent issues.
6.4
The Prevention and Control of Water Pollution During
the 11th Five-year Plan
6.4.1 Wastewater Compliance Rate
In Fig.
6.2
, from 2001 to 2010, because of the rapid development of economy,
industrial production increased, and the national wastewater emissions rose slowly.
Chemical oxygen demand total emissions and ammonia emissions declined, but not
significantly.