Database Reference
In-Depth Information
High Availability and Database Virtualization
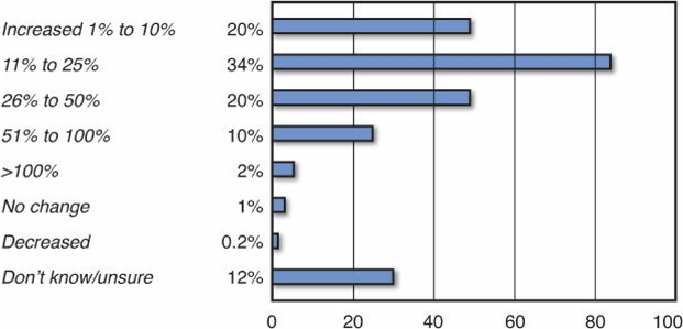
Numerous industry reports document the fact that a typical production database will
double in size every three years. As you can see in
Figure 2.3
, the Petabyte Challenge:
2011 IOUG Growth Survey shows how databases keep getting bigger and more
complex. The IOUG Research Wire study was produced by Unisphere Research, a
Division of Information Today. This survey is available at no charge from Database
Trends & Applications (
www.dbta.com
).
Figure 2.3
The Petabyte Challenge: 2011 IOUG Database Growth Survey. “The
Petabyte Challenge: 2011 IOUG Database Growth Survey” was produced by Unisphere
Research, and sponsored by Oracle. Figure provided courtesy of Unisphere Research, a
Division of Information Today, Inc. and the Independent Oracle Users Group (IOUG).
As these databases get bigger and more complex, the ability to recover also becomes
more complex. With virtualization, you have redundancy up and down the entire
infrastructure stack. By maintaining a high level of redundancy, you can avoid a
situation where you would have to perform a database recovery in the first place.
Figure 2.4
illustrates the many levels of redundancy you have when your database is
virtualized. For example, if a network interface card (NIC) or even a port were to fail,
the VMware hypervisor would detect the failure and reroute traffic to another available
port. If a host bus adapter (HBA) path were to fail, the VMware hypervisor would
detect the failure and reroute the request to the storage system another way. Best part,
all this is built in to the hypervisor and is transparent to the database and applications.