Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Note
For more information on Leaf-Spine architecture, see the following
references:
05/jt893/12022/97352/Arista_Cloud_Networks.pdf
.
Figure 8.19
uses Multi-Link Aggregation Group (MLAG) between the spine switches,
which is suitable on a small scale. Larger-scale designs would typically utilize Equal-
Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) between the Leaf and Spine nodes.
Network I/O Control
distributed switch allows for different traffic types to be prioritized at the host level to
ensure that each type of traffic gets its fair share of network resources. It is based on a
proportional share algorithm, which allows it to adjust to different traffic patterns
dynamically and not limit any one type of traffic if there is no congestion. This avoids
having to set any hard limits and allows much more effective pooling of network
resources across physical NICs and hosts.
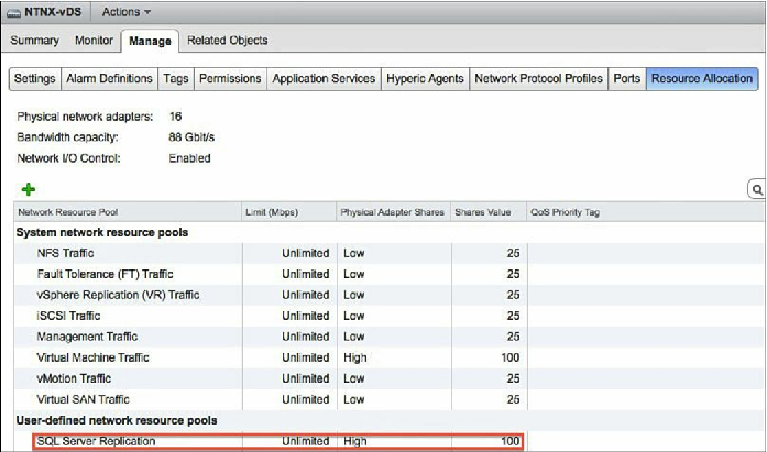
Figure 8.20
shows an NIOC configuration
with a user-defined resource pool for SQL Server replication traffic.
Figure 8.20
Network I/O Control resource pools.