Database Reference
In-Depth Information
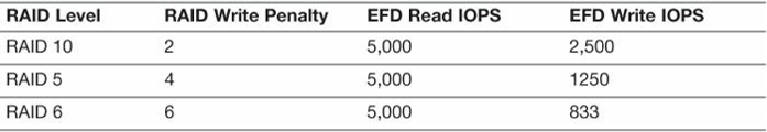
Table 6.16
RAID IO Penalties During Normal Operations of Enterprise Flash Disk
Table 6.16
assumes a performance level of 5,000 IOPS for a single EFD disk.
Depending on the type of EFD or SSD, these numbers could be very different. You
should check with your particular vendor for their latest numbers. Also, it's quite
common for the read and write performance to be different even without the RAID
penalties.
Table 6.17
shows the number of EFD disks required at different RAID levels to meet
the IOPS as well as the capacity requirements of our sample SQL database workload.
Table 6.17
EFDs at Different RAID Levels Required for Example SQL DB
Table 6.17
illustrates the number of EFDs required to meet both the performance and
capacity requirements of our sample SQL DB. In this example, the RAID 5 option is the
most cost effective from a performance and capacity perspective.
Comparing the number of 400GB EFDs required to meet the SQL requirements against
the most cost effective options for spinning disks (Gold Policy RAID 10), we can see
that we need five times less EFDs. For this workload, the eight EFDs may be the best
option if their combined cost is less than the 40 spinning disks. In many cases, the EFDs
will be less cost, especially when the reduced space, power consumption, and cooling
of EFDs is considered.
Let's add a Platinum storage policy in addition to the previous defined policies and
calculate the effective IOPS per TB based on our 400GB EFD example.
With the new Platinum storage policy in
Table 6.18
,
we can easily meet the
performance requirement of 5000 IOPS, but we need additional disks to meet the
capacity requirement.
Table 6.15
shows us that we need eight EFDs at 400GB in order
to achieve the required 2.5TB. Based on provisioning 2.8TB of usable capacity, we can
calculate that our achievable IOPS from that capacity at a conservative 4000 IOPS per
TB at RAID5 with write penalty of 4 is 11,200 IOPS. At this point, it's likely that we'd
run out of capacity well before running out of performance.