Database Reference
In-Depth Information
take into account your availability requirements and risks, as the loss of access to
a single data store in this case could impact multiple SQL systems. Backup disks
can be shared with the same IO controller as the OS, and we recommend they are
on their own VMDK and data store if their size and performance requirements
justify it.
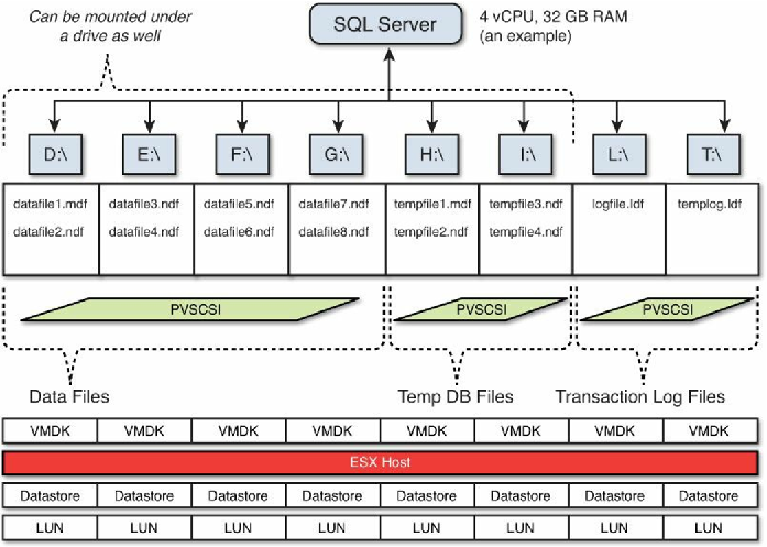
The example in
Figure 6.18
shows each VMDK mapped to a dedicated data store. This
layout is suitable for SQL systems that need extreme IO performance and scalability. It
allows IO to be spread across more storage devices, and each VMDK has access to the
maximum possible amount of parallel IO. The increased number of data stores and
therefore LUNs will limit the total number of VMs that can be supported per host. You
will have many more data stores to manage per VM, which will increase your
management overheads.
Figure 6.18
Single VMDK per data store.
If each SQL VM has 10 data stores, you could be limited to just 25 VMs per cluster, as
each data store should be zoned to each host in the cluster to allow VMware HA and
DRS to function correctly. It is likely that if you need this layout for storage