Database Reference
In-Depth Information
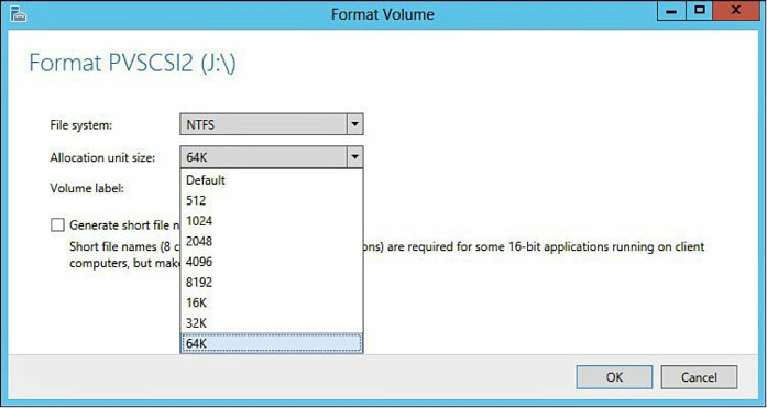
recommend you use 64KB as your Allocation Unit Size setting (see
Figure 6.7
).
Figure 6.7
NTFS Allocation Unit Size.
Tip
The Default NTFS Allocation Unit size is 4KB for all volumes up to 16TB in
size. Volumes greater than 16TB in size will have larger default Allocation Units.
Regardless of your volume size and the default NTFS Allocation Unit size, we
recommend you use 64KB. For most environments, it's unlikely you will be using
more than 16TB for each volume.
See
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/140365
for further details of the NTFS
Allocation Unit sizes for different-sized volumes.
Partition Alignment
Each storage device reads and writes data at different underlying block sizes. A block
on a storage device is the least amount of data that is read from or written to with each
storage option. If your file system partition is not aligned to the underlying blocks on the
storage device, you get a situation called Split IO in which multiple storage operations
are required to service a single operation from your application and operating system.
Split IOs reduce the available storage performance for productive IO operations, and
this gets even worse when RAID is involved, due to the penalty of certain operations,
which we'll cover later in this chapter.
Figure 6.8
shows what would be considered a worst-case scenario, where the file