Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Need
co-allocation
Receive
request
[yes]
Check request
[no]
Search for all
potential resources
Create offer
Make selection
FIGURE 7.4
Creation of local offer.
Figure 7.4 describes how to generate local offers. Users or clients send
out a request to the MetaManager. The necessary scheduling require-
ments and job attributes, such as the run time, the required number of
resources, the earliest start time, and the latest end time, are included in
each request. When the local MetaManager receives this request, it extracts
this information and searches the local domain to i nd whether the local
resources can meet the job's requirements and whether the user's budget
is enough to process the job. If there are sufi cient resources in the local
domain to support the job, the scheduler will i nd the best-i tted resource
to execute the job; otherwise, multisite scheduling will be initiated.
The scheduler i rst collects all the free-time intervals of each resource.
Since one free-time interval normally cannot satisfy the job's require-
ments, combinations of intervals need to be considered. The deviation of
bucket sort is used to combine the intervals. For example, all the intervals
with the same start time can be collected into one bucket. Then the selec-
tion is made again to collect the intervals with the same end time from
that bucket. As a result, a combination of intervals with the same start
time and end time is generated. If there are several combinations fuli lling
the requirements, the scheduler can select the one with the highest utility
value based on some heuristics.
When there is no single resource able to execute the application by itself,
the local scheduler sends the request to the remote MetaManager to gener-
ate multisite co-allocation. In this case, the job will be divided into several
small parts as specii ed by some parameters. However, several aspects of
the grid, such as the site autonomy and cost management, must be taken
into account. This economic scheduling approach provides support for
individual access and services. It combines the independent domains and
limits the failure impact in the local area. With this system, co-allocation of
resources from different sites with different scheduling is possible.
7. 4 . 4
Peer-to-Peer Method
Peer-to-peer (P2P) systems and grids are two resource-sharing environments.
Although they differ in their usages, they both link resources and people
with physically distributed locations within virtual organizations (VOs).




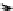







Search WWH ::

Custom Search