Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
•
Accuracy and completeness: FTGP identii es faults accurately,
with lower false positives and false negatives.
Simplicity: FTGP provides toolkits to solve any type of faults in
•
grid systems, and provides a virtual interface for grid users.
4.5.2.1
Fault-Tolerant Grid Topology
In grid systems, there are two types of hardware failure: node crashing
and network appliance. It is quite difi cult for application developers to
determine when no remote response arises from node crashing or network
failure. To cope with this, FTGP constructs a network with fault-tolerant
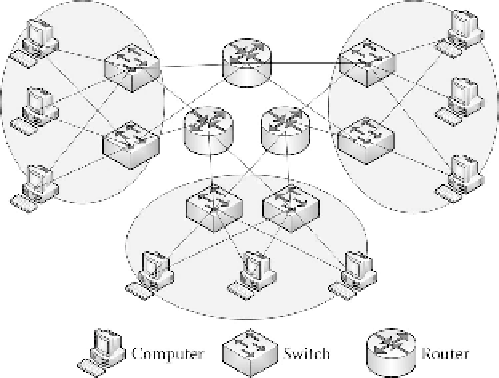
topologies. A simple network topology with fault-tolerant features is shown
in Figure 4.5. Any two single machines have two routes in a fault-tolerant
grid system.
In order to prevent one network interface card (NIC) in a single machine
from crashing a single point of failure, two NICs are required for one
machine. Under this network architecture, two routes for any end-to-end
information would not overlap with each other at the same network appli-
ance. Any network appliance failure would not affect network communi-
cation of the grid. Based on this network topology, FTGP detects the
network appliance status based on simple network management protocol
(SNMP) [43]. Double links provided by such a topology reduce the unreach-
ability of a machine. For a node crash, FTGP should not only recover appli-
cations and tasks from those failed nodes by transferring them to other
correct grid nodes, but also dynamically extend the grid system to provide
FIGURE 4.5
A simple network topology with fault tolerance.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search