Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
produced a resultant force that underpredicted the experimental EAF response.
This variation is due to the model not incorporating thermal expansion effects.
6.3 Thermo-Mechanical Model
In this section, the local material strain, flow stress, and thermal profile are pre-
dicted for EAF of sheet metal in uniaxial tension. This is accomplished by com-
bining the thermal model with the deformation/strength model. Additionally,
thermal expansion effects are incorporated as they also introduce stress to the
material. The division of electrical energy applied to the workpiece during EAF is
also divided between bulk thermal softening and direct electrical effects.
6.3.1 Thermo-Mechanical EAF Model Overview and
Solution Scheme
The thermo-mechanical EAF model incorporates bulk thermal softening effects, direct
electrical effects (i.e., electroplasticity), and thermal expansion effects to predict the
local material strain, flow stress, and thermal response of sheet metal during EAF. The
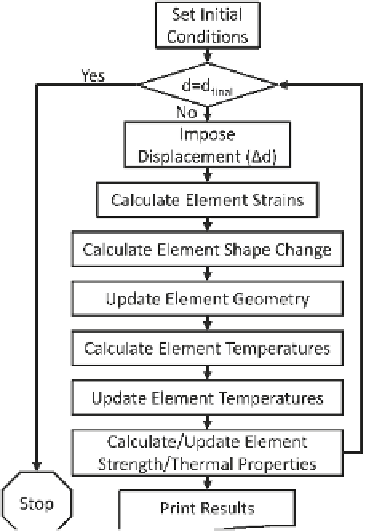
model solution scheme is given in Fig.
6.38
. First, the initial conditions are set for the
Fig. 6.38
Multi-physics
EAF model solution scheme