Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
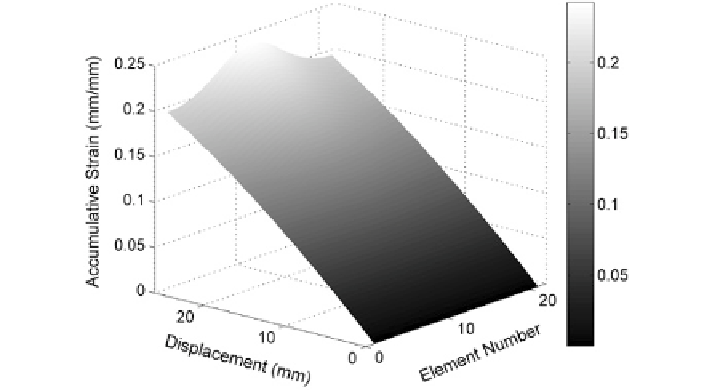
Fig. 6.30
Accumulative strain results for EAF diffuse thermal model input for PS 4
compared to the elements at a lower temperature (i.e., near ends). Also, as the
material cools after the electrical pulse, it is shown that the incremental strain for
each element approaches each other as the strength properties become similar.
As a result of varying incremental strain results from the simulation, the accu-
mulative strain over time will not be equal for each element. The accumulative
strain for each element is presented in Fig.
6.30
. As seen, the center elements with
greater incremental strain have a larger amount of strain imposed over time (i.e.,
accumulative strain). Also, the simulation solution does not begin to show a sig-
nificant amount of localized straining until near the end of the simulation. This can
be attributed directly to the input temperature distribution where there is a much
larger thermal gradient along the length at the end (i.e., >15 mm of total imposed
displacement).
Due to the diffuse accumulative strain, the length and area of each element will
vary at a given total input displacement. These results for element length and area
are presented in Figs.
6.31
and
6.32
, respectively. The element length is directly
derived from the accumulative strain; thus, the overall profile shape is the same.
For the area, the elements with more strain (i.e., center) have a smaller cross-
sectional area due to the length of the element being greater.
The stress response from the simulation is given in Fig.
6.33
. As seen, during
the application of current (i.e., temperature rise), the true stress of the material sig-
nificantly decreases as a result of the material being in a weaker state.
The stress response for each element at a given time step may not be equal due
to the elements having different cross-sectional areas. This is seen where the ele-
ments with a smaller cross-sectional area (i.e., center) have a greater stress than
the elements with a larger cross-sectional area (i.e., ends).