Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
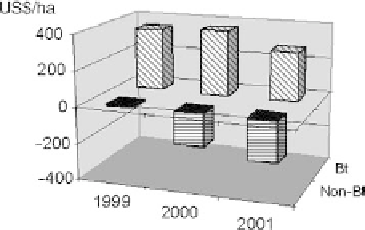
Figure
12.13.
Net revenue of Bt and non-Bt cotton in China. (Adapted from work cited in
Ref. 14.)
variety. Analysis of the economic benefits in Figure 12.13 shows the real reason for this
rapid adoption. Farmers using Bt cotton had net profits of US$277 to US$367 per
hectare during the period studied. Increased yields were only part of the reason
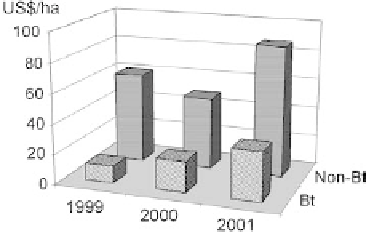
for increased profitability. Insecticide costs were reduced more than half, as
shown in Figure 12.14. In addition to the increased profitability, the number of reported
insecticide poisonings by farmers using Bt cotton were significantly reduced.
The adoption of transgenic crops has been slowed by the refusal of some markets to
accept transgenic food grains. In most cases these countries have initiated a study of the
safety of transgenic foods before they are permitted to enter the human food chain.
There are signs that official restrictions are slowly being reduced and markets will
open for more transgenic crops. Various international accords have been reached to
help supervise or control the introduction of modified crops and animals.
15
The Con-
vention on Biological Diversity is concerned with the conservation and the sustainable
utilization of ecosystems. This convention adopted the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety
in 2003 to give advance notice before the introduction of transgenic plants that may
have adverse environmental effects. This notice is registered with the international
Biosafety Clearing House. Another international agreement is the International Plant
Protection Convention. This agreement attempts to prevent the spread of pests affecting
cultivated plants. Specifically, it seeks to prevent the introduction of traits that
may cause some plants to become invasive (unwanted spreading to cultivated areas).
Figure
12.14.
Pesticide costs on cotton in China. (Adapted from work cited in Ref. 14.)