Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Papaya fruit on a papaya plant is shown in Figure 6.9. Certain fruits are produced on
bushes or bushlike plants, while pineapple (Fig. 6.10) is its own unique type of plant.
Some berries are produced on brambles while others are produced on low-growing
vine-type plants. Each of these, and other unique fruit, berry, or nut production charac-
teristics will be discussed in the appropriate section below.
Cultivation, fertilization, protection, harvesting, transport, and storage character-
istics of other fruits and berries are basically the same as for tree fruits as discussed
in above sections.
6.4
TROPICAL FRUITS
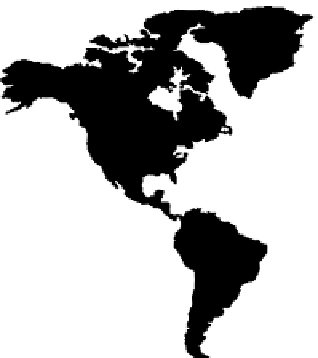
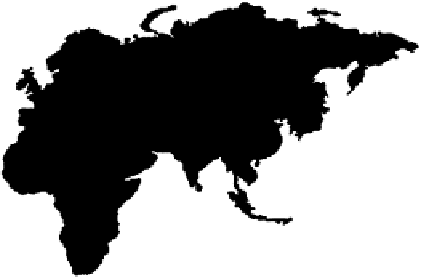
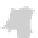
Tropical-fruit-producing countries are shown in Figure 6.11, which was produced by
summing FAO data on world production of avocado, banana, kiwi, mango, papaya,
and pineapple. Tropical fruits are produced on trees and on a number of other different
types of plants, which in some cases look like trees although they are botanically very
different from a true tree.
6.4.1 Tropical Tree Fruits
Tropical fruits, three common examples of which are shown in Figure 6.12, are similar
in size and stature to other fruits and grow on trees similar to other fruit trees. There is
one striking difference in that some of these fruit trees bear fruit on stems on the trunk
of the tree rather than on stems along or on the end of branches. One common occur-
rence of this type of fruit production is the jackfruit, as pictured in Figure 6.13. Another
difference is that the fruit comes in forms that are quite different from one another.
Figure
6.11.
Map of countries producing tropical fruits. (From FAO data at http:
//
faostat.fao.
org
/
default.aspx.)