Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
5.3
ROOT CROPS
Root crops include all crops where the main edible portion grows below ground.
†
In this
chapter we will discuss tubers, which are modified roots, enlarged roots, and the below-
ground modified enlarged stems called corms. Of the root crops, worldwide the potato
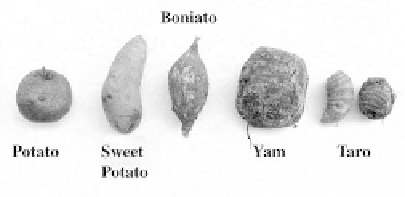
and sweet potato, shown in Figure 5.4, which are tubers, are the best known and most
widely grown. Examples of the major types of root crops discussed in this chapter are
shown in Figure 5.4.
In addition to potatoes and sweet potatoes, there are many other types of root crops
that are important and form a substantial portion of the diet in much of the world. Yam
(a tuber), cassava (a root), and taro (a corm) are examples of three that are both common
and important foods in many tropical countries, Pacific and Caribbean islands, and in
countries in Africa. Yam is eaten like and often substituted for sweet potato in
cooking; cassava is used to make flour used in baking breads, cakes, and pies. Taro,
also called coco yam, is cooked by boiling, baking, frying, or roasting. It is also used
to make poi in Hawaii and is considered a sacred plant to native Hawaiian islanders.
In addition to the below-ground portion of the plant, boniato and taro leaves are com-
monly boiled and eaten. Cassava leaves are also eaten, however, this use is restricted
primarily to areas of Africa.
While the potato is a well-understood name that applies to the same root crop
around the world, the same cannot be said for the other root crops. The same name
may be applied to two different crops or different names may be applied to the same
crop. For instance, sweet potato may be called yam or boniato and cassava may also
be called yucca. In addition each local language may have several names for the
same crop, and different names may be used in different regions. It is not within the
scope of this topic to try and separate and identify all the different names and ways
these names are used. The names that are commonly used (Fig. 5.4) will be the ones
used throughout this chapter.
Figure
5.4.
Examples of tuber crops, potatoes, sweet potatoes, boniato, yam, and taro.
†
The peanut grows below ground but is generally not considered a root crop because it grows on a stem that
grows into the ground from the above-ground portion of the plant.