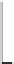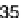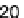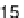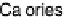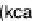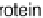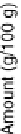Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
All are generally oblong or round in shape and the outside, the rind, may be yellow as
with pumpkin or green as with zucchini. The interior may be solid with seeds imbedded
in the flesh or hollow with seeds on the inside. Seeds can be eaten in the fresh young
vegetable, such as with cucumber and zucchini, or separated, cooked, and eaten as
with pumpkin seeds.
4.9.2 Importance in Human Nutrition
These vegetables are higher in calories and carbohydrates than other nutrients, as
shown in Figure 4.19. Protein content is second highest, although still low, followed
by fiber. Fat content is very low ranging from 0.1 to 0.18 percent.
4.9.3 Soil Preparation and Cultivation
For melon and cucumber production soil is prepared as for other vegetables. Organic
matter and fertilizer is be added to soil and soil pH adjusted as needed. Depending
on the planting method, soil may be left flat, worked into ridges, raised beds, or
hills. Regardless of the method of preparation, mulch is commonly used to control
weeds, water, and where vines are on the ground, to protect the developing melons
or cucumbers.
Cultivation of cucumbers and melons is different from other crops because these
crops typically grow on vines that spread over the ground. Most vegetable crops
grow on upright plants, and soil can be planted in rows and cultivated between rows
Figure
4.19.
Nutrient values of melons, squash, and cucumber. (From data in USDA National
Nutrient
Database
for
Standard
Reference,
Release
17.
http:
//
www.nal.usda.gov
/
fnic
/
foodcomp
/
Data
/
SR17
/
reports
/
sr17page.htm.)