Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
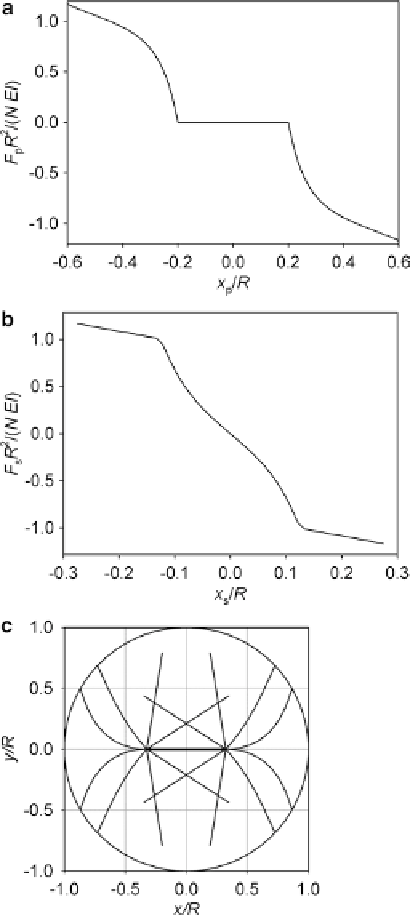
Fig. 7
Limiting case of
q
max
= π, short microtubules.
(
a
) Pole force function.
(
b
) Spindle force function.
(
c
) Equilibrium
conformation.
L
= 0.8
R
,
S
= 0.65
R
. For clarity, only
few microtubule forms are
plotted. These microtubules
lie in the (
x
,
y
) plane that
passes through the spindle
axis. Their values of
q
are
sampled uniformly between 0
and
q
max
. Reproduced from
Maly (
2012
) under the
Creative Commons
Attribution License
The positioning of an isolated complete aster with comparatively long microtu-
bules in three dimensions was considered in the previous section (Figs.
2
and
3
). In
this case, considered now as a model for an isolated spindle pole, the pole force func-
tion has a root at approximately
x
p
= 2(
L
−
R
): A more centrally positioned pole is
attracted to the cell margin, whereas a more eccentrically positioned one is repelled.
Considering a spindle with such an aster at each pole, one can observe that the pres-
ence of the root does not affect the stability of symmetry. Even though the pole force