Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
The Commission consists of seven Commissioners - four (including the chairman)
nominated by the Australian Government, and three nominated jointly by the states and
territories. Unique among Australian intergovernmental institutions, Commissioners are
appointed for their expertise in a range of water-related fields (including freshwater
ecology, hydrology, resource economics, and public sector management) rather than as
representatives of sectoral or government interests. The Commission is supported by a
small staff of just over 40.
The National Water Commission has three main functions:
assess governments' progress in implementing the NWI (e.g. through biennial
assessments of progress commencing in 2006-07);
help governments to implement the NWI (e.g. by acting as lead facilitator on certain
actions under the NWI such as nationally compatible registers of water entitlements and
trades, and nationally consistent approaches to pricing); and
administer two programmes under the Australian Government Water Fund (including
recommending projects for decision by the Australian Government on financial
assistance from the Water Smart Australia programme and the Raising National Water
Standards programme).
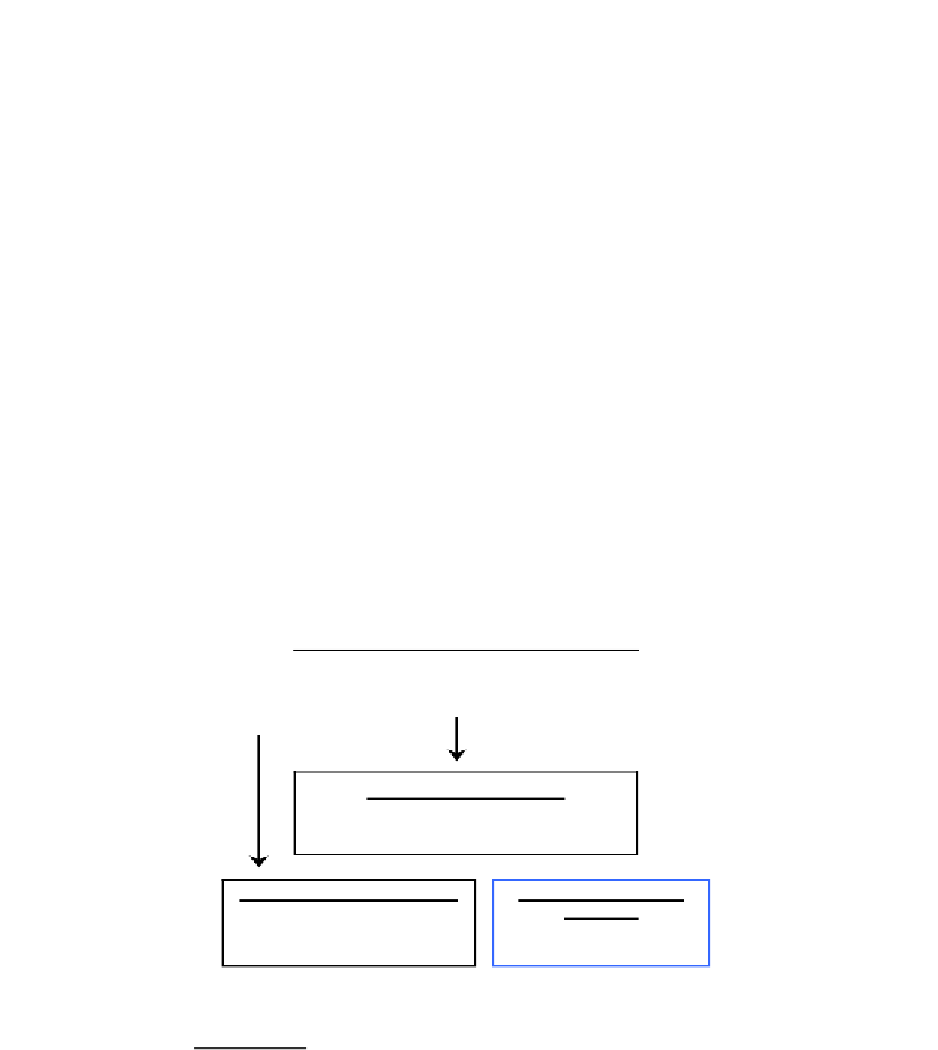
Figure 1. The Australian Government Water Fund (AGWF)
Australian Government Water Fund
$2b over 6 years 2004-05 to 2009-10
Administered by NWC
Water Smart Australia
$1.6b over 6 years 2004-05 to
2009-10
Raising National Water Standards
Programme
$200m
Administered by NWC
Community Water Grants
Programme
$200m
Administered by DEH/DAFF
Further detail on the roles of the National Water Commission and the Australian Government Water Fund
can be found at www.nwc.gov.au.
Market, regulatory and planning based systems for water management
As noted above, the NWI recognises that water in Australia is managed through a
combination of instruments including market, regulatory and planning based systems.
Any discussion of the economics of water management in Australia needs to recognise
these complementary and competing instruments. To illustrate, examples of each of these
types of instrument follow.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search