Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
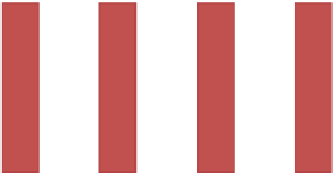
Fig. 13.1
Discrete
distribution
f
(x)
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
X
0
2
3
1
4
Fig. 13.2
Even distribution
f
(x)
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
X
1
2
3
4
13.8.3
Normal Distribution
The best opportunity for using the normal distribution (Fig.
13.3
) which is an impor-
tant and commonly used distribution is when the modeler purpose is to explain a
physical data such as distance or temperature. In this method approximately 68 %
of the probable values that a variable can take are within one standard deviation of
the mean value, 95 % are within two standard deviations of the mean and 99.5 %
within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
When mean value
2
= 1),
then the distribution is known as standard normal distribution. Usually it is assumed
that for normally distributed variables, combination of independent normally dis-
tributed random variables also distributed according to the normal distribution.
Random number generation for normally distribution function can be done based
on different methods, e.g., trapezoidal method, polar method, and histogram method
(McDonald
2002
).
The normal distribution is often called Gaussian distribution or bell curve.
ʼ
= 0 and standard deviation value
˃
= 1 (variance value
˃