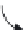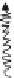Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Rotating arm
Influent spray
Rock bed
Influent
Underdrain
system
Euent
figure 7.3 Schematic of cross-section of a trickling filter.
Influent flow
Organic matter
Zoogleal slime
Media
Sloughing
Oxygen
Air
figure 7.4 Filter media showing biological activities that take place on
the surface area.
high-rate trickling ilters—
A classification (see Table 7.1) in which the
organic loading is in the range of 25 to 100 lb of BOD
5
per 1000 ft
3
of media per day. The standard-rate filter may also produce a highly
nitrified effluent.
hydraulic loading—
The amount of wastewater flow applied to the
surface of the trickling filter media. It can be expressed in several
ways: flow per square foot of surface per day (gpd/ft
2
), flow per acre
per day (MGAD), or flow per acre foot per day (MGAFD). The hydrau-
lic loading includes all flow entering the filter.
media—
An inert substance placed in the filter to provide a surface
for the microorganism to grow on. The media can be field stone,
crushed stone, slag, plastic, or redwood slats.