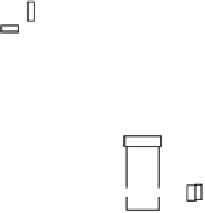Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Plug-type disk
angle valve
Pressure
gauge
Safety
valve
Pressure-regulating valve
Gate valve
Gate valve
figure 4.37 Temperature-regulating valve assembly.
may develop. Relief
valves are used to control this excess pressure. Such
valves are automatic valves; they begin to open at a preset pressure but
require a 20% overpressure to open wide. As the pressure increases, the
valve continues to open farther until it has reached its maximum travel.
As the pressure drops, it starts to close and finally shuts off at about the
set pressure. Main system relief valves are generally installed between
the pump or pressure source and the first system isolation valve. The
valve must be large enough to allow the full output of the hydraulic pump
to be delivered back to the reservoir.
Note:
Relief valves do not maintain flow or pressure at a given amount
but prevent pressure from rising above a specific level when the system
is temporarily overloaded.
4.13.2.12 Pressure-Reducing Valves
Pressure-reducing valves provide a steady pressure into a system
that operates at a lower pressure than the supply system. In practice,
they are very much like pressure-regulating valves. A pressure-reducing
valve reduces pressure by throttling the fluid flow. A reducing valve can
normally be set for any desired downstream pressure within the design
limits of the valve. Once the valve is set, the reduced pressure will be
maintained regardless of changes in supply pressure (as long as the
supply pressure is at least as high as the reduced pressure desired) and
regardless of the system load, providing the load does not exceed the
design capacity of the reducer.
4.13.3 valve operators
In many modern wastewater operations, devices called
operators
or
actuators
mechanically operate many valves. These devices may be
operated by air, electricity, or fluid—that is, by pneumatic, hydraulic,
and magnetic operators.