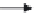Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
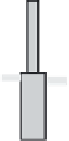
Handwheel
Stem
Closing
element
Stuffing box
Body
Outlet
Inlet
Open
Closed
figure 4.32 Basic valve operation.
4.13.1 valve Construction
Figure 4.32 shows the basic construction and principle of operation
of a common valve type. Fluid flows into the valve through the inlet. The
fluid flows through passages in the body and past the opened element
that closes the valve. It then flows out of the valve through the outlet or
discharge. If the closing element is in the closed position, the passageway
is blocked. Fluid flow is stopped at that point. The closing element keeps
the flow blocked until the valve is opened again. Some valves are opened
automatically, whereas manually operated hand wheels control others.
Other valves, such as check valves, operate in response to pressure or
the direction of flow. To prevent leakage whenever the closing element is
positioned in the closed position, a seal is used. In Figure 4.32, the seal
consists of a
stufing box
fitted with packing. The closing element fits
against the
seat
in the valve body to keep the valve tightly closed.
4.13.2 Types of valves
The types of valves covered in this text include:
• Ball valves
• Gate valves
• Globe valves
• Needle valves
• Butterly valves
• Plug valves
Check
•
valves
• Quick-opening valves
• Diaphragm valves
• Regulating valves
• Relief valves
• Reducing valves