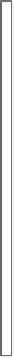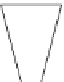Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
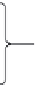
Hollow
shaft motor
Discharge head
Stung box
Driving shaft
Bowl
Pump unit
Impeller
Suction bell
Screen
figure 3.16 Vertical turbine pump.
3.3.9.3.2 advantages
The turbine pump has a major advantage in the amount of head it is
capable of producing. By installing additional impeller-bowl assemblies,
the pump is capable of even greater production. Moreover, the turbine
pump has simple construction and a low noise level and is adaptable to
several drive types—motor, engine, or turbine.
3.3.9.3.3 disadvantages
High initial costs and high repair costs are two of the major disad-
vantages of turbine pumps. In addition, the presence of large amounts of
solids within the liquid being pumped can seriously increase the amount
of maintenance the pump requires; consequently, the unit has not found
widespread use in any situation other than service water pumping.
3.4 PosiTive-disPlaCeMenT PuMPs
Positive-displacement pumps
force or displace water through the
pumping mechanism. Most have a reciprocating element that draws water
into the pump chamber on one stroke and pushes it out on the other.
Unlike centrifugal pumps that are meant for low pressure, high-flow appli-
cations, positive-displacement pumps can achieve greater pressures but
are slower moving, low-flow pumps. Other positive-displacement pumps
include piston pumps, diaphragm pumps, and peristaltic pumps, which