Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
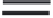
figure 3.13 Thermocouple installation in journal bearing.
the discharge rate for a centrifugal pump. This type of control may use
one of the previously described controls to start and stop the pump and,
in some cases, adjust the speed of the unit. As the depth of the water in
a well or tank increases, the sensor automatically increases the speed
of the motor in predetermined steps to the maximum design speed. If
the level continues to increase, the sensor may be designed to activate
an additional pump.
3.3.8.4 Protective Instrumentation
Protective instrumentation of some type is normally employed in
pump or motor installation. (Note that the information provided in this
section applies to the centrifugal pump as well as to many other types
of pumps.) Protective instrumentation for centrifugal pumps (or most
other types of pumps) is dependent on pump size, application, and the
amount of operator supervision; that is, pumps under 500 hp often only
come with pressure gauges and temperature indicators. These gauges or
transducers may be mounted locally (on the pump itself) or remotely (in
suction and discharge lines immediately upstream and downstream of
the suction and discharge nozzles). If transducers are employed, read-
ings are typically displayed and taken (or automatically recorded) at a
remote operating panel or control center.
3.3.8.5 Temperature Detectors
resistance temperature devices
(RTDs) and
thermocouples
(see
Figure 3.13) (Grimes, 1976) are commonly used as temperature detectors
on the pump prime movers (motors) to indicate temperature problems. In
some cases, dial thermometers, armored glass-stem thermometers, or
bimetallic-actuated temperature indicators are used. Whichever device
is employed, it typically monitors temperature variances that may indi-
cate a possible source of trouble. On electric motors greater than 250 hp,
RTD elements are used to monitor temperatures in stator winding coils.
Two RTDs per phase are standard. One RTD element is usually installed
in the shoe of the loaded area employed on journal bearings in pumps
and motors. Normally, tilted-pad thrust bearings have an RTD element
in the active, as well as the inactive, side. RTDs are used when remote
indication, recording, or automatic logging of temperature readings is
required. Because of their smaller size, RTDs provide more flexibility
in locating the measuring device near the measuring point. When dial