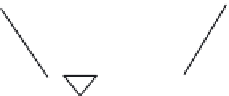Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
Rectangle weir
Head
Weir crest
Crest length
(B)
Triangular weir
V-notch angle
Head
Weir crest
figure 2.35 (A) Rectangular weir and (B) triangular V-notch weir.
Example 2.17
Problem:
A weir 4-ft high extends 15 ft across a rectangular channel in
which the water is flowing at 80 cfs. What is the depth just upstream
from the weir?
Solution:
q
= 3.33 ×
l
×
h
1.5
80 = 3.33 × 15 ×
h
1.5
h
= 1.4 ft (with calculator, 1.6 INV
y
x
1.5
= 1.36, or 1.4)
4 ft (height of weir) + 1.4 ft (head of water) = 5.4 ft (depth)
Triangular weirs
, also called
v-notch weirs
, can have notch angles
ranging from 22.5° to 90°, but right-angle notches are the most common
(see Figure 2.34B). The formula used for V-notch (90°) weir calculations
is:
q
= 2.5 ×
h
2.5
(2.28)
where:
q
= flow.
h
= head on weir (measured from bottom of notch to water surface).
Example 2.18
Problem:
What should be the minimum weir height to measure a flow of
1200 gpm with a 90° V-notch weir if the flow is moving at 4 ft/s in a 2.5-ft
wide rectangular channel?