Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
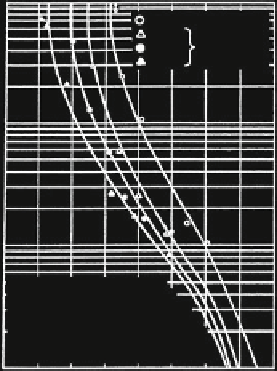
Fig. 2.44 Number of rope
cycles N for cross lay ropes
6 9 19-FNC—sZ with
different diameters, Müller
(
1966
)
10
6
1960 N/mm
2
1570 N/mm
2
2,5
ˆ
5
7
ˆ
16
ˆ
28
ˆ
5
3
2
10
5
7
5
3
2
10
4
7
5
cross lay ropes
6 19 - NFC - sZ
lubricated
˃
z,lower
= 50 - 60 N/mm
2
3
2
10
3
0
400
600
800
1000
N/mm
2
1400 1600
200
range of rope stress 2
˃
2.6.4 Further Results of Tension Fatigue Tests
2.6.4.1 Number of Load Cycles for Wire and Wire Rope
Setzer (
1976
) did tension fatigue tests with a Warrington-Seale rope and compared
them to the strands and wires of this rope before being manufactured into a rope.
He presented the result of these tests as a Smith diagram shown here in Fig.
2.42
.
The diagram is based on a number of load cycles N = 2 9 10
6
. For the middle
stress r
m
= 500 N/mm
2
Setzer found a stress range 2r
a
= 550-600 N/mm
2
for
the wires and only 2r
a
= 140 N/mm
2
for the wire rope.
A further comparison of the stress range for the wires and the wire rope is
shown on the basis of the data of Table
2.9
for the Warrington-Seale ropes. Fig-
ure
2.43
shows the stress range in the outside wires for a rope with the diameter
d = 16 mm where the wire rope breaks at the number of load cycles N = 10
6
,
with a probability of 1, 10 or 50 %. In order to take the additional stresses into
consideration, the stress range for the wire rope (better for the outside wires of the
rope) has been drawn 20 % above the global wire rope stress r
z
= S/A
m
calculated
using (
2.102
). In comparison, the strength range for straight wires with the same
diameter as the outside rope wires is drawn in Fig.
2.43
. This strength range has
been calculated with (1.3) and (1.3b) for a breakage probability of 50 %.
Even for a high quality wire rope (failure probability 1 %), the stress range for
the breakage at the number of load cycles N = 10
6
is clearly smaller than the mean
stress range of the straight wires. The remaining difference can be declared by the
unsystematic increased stresses of individual wires or strands due to the loosening
of the others, Evans and others (
2001
). Furthermore, the pressure between the
wires has not been included in the stress calculation.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search