Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10
7
specific force range
rope number N
rope diameter d = 16 mm
2S
a
/s
2
= 250 N/mm
2
S
o
/d
2
= 0.5 F
r
/d
2
300 N/mm
2
10
6
10
5
350 N/mm
2
10
4
0
100
200
300
400
lower spec. tensile force S
lower
/d
2
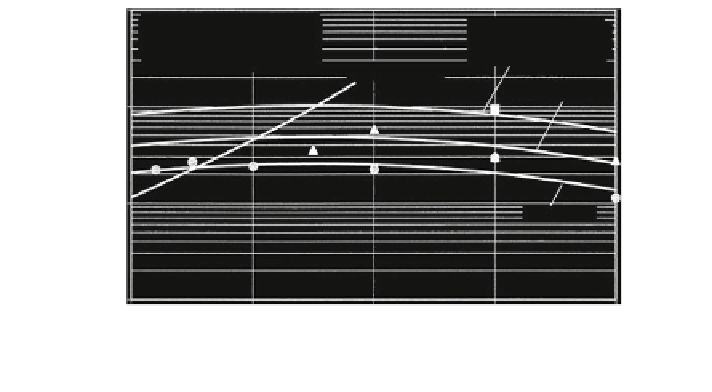
Fig. 2.41
Number of load cycles of an open spiral rope 1 9 37, Wehking and Klöpfer (
2000
)
with open spiral ropes. In all cases the wire ropes were fastened in resin sockets.
The results of these tests have been evaluated by regression with (
2.102
). The
constants and the rope and test data are listed in Table
2.8
.
Wehking and Klöpfer (
2000
) and Klöpfer (
2002
) tested open spiral ropes with
round wires 1 + 6 + 12 + 18 (short 1 9 37) with different diameters. The free
length between the sockets was uniformly L = 40d. The wire ropes had zinc
coated wires and were lubricated. The numbers of load cycles up to
N = 1.75 9 10
6
are included in the regression calculation. For every wire rope,
the coefficient of determination is high but the standard deviation varies between
lg s = 0.094 and 0.236. The constants a
i
in Table
2.8
determined by Wehking and
Klöpfer (
2000
) was corrected slightly by Klöpfer (
2002
) by neglecting the results
with rope breakages near the terminations. This then reduces the standard devia-
tion to lg s = 0. 227.
The maximum number of load cycles has been reached for the mean lower
specific force S
lower
/d
2
= 140 N/mm
2
with a relatively large deviation. The
numbers of load cycles for a spiral rope with the diameter d = 16 mm are pre-
sented in Fig.
2.41
as an example. The line for the upper force as a half rope
breaking force has been included in the figure to show the maximum usable region.
It can be seen in Fig.
2.41
that the endurance curves are relatively flat. In
accordance to that Alani and Raoof (
1997
) found that under fluctuating tensile
forces the endurance of spiral ropes has been nearly independent from the lower
respectively the middle stress.
Two of the seven wire ropes tested had the unusual wire lay direction SSZ. In
comparison with the normal lay direction ZSZ, the wire lay direction SSZ has
lower endurance.
Casey (
1993
), and Paton et al. (
2001
), National Engineering Laboratory (NEL)
East Kilbride, Glasgow, have done numerous tension-tension fatigue tests with
Search WWH ::

Custom Search