Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in the same way with the usual lubrication. There was virtually no difference in the
rope bending endurance documented for the original tests and the new tests. For
two of these wire ropes, the mean strength of the wires was reduced during the
long period of storage by a maximum of 3 %. For one rope, the mean strength of
the wires increased by 2.7 %.
1.1.2 Wire Manufacturing
After the rod has been patented in a continuous system, the wire diameter is
reduced in stages by cold drawing or cold rolling, rolling especially for profile
wires. Patenting is a heating process. First the wire is heated in an austenising
furnace at about 900 C. Then the temperature is abruptly reduced to about 500 C
when the wire is put through a lead bath. After remaining there for a while,
the wire then leaves the bath and enters the normal temperature of the surround-
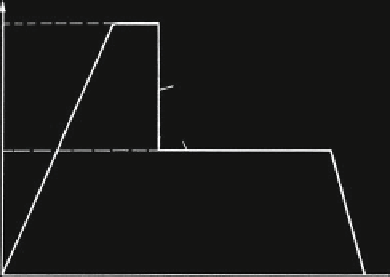
ings. Figure
1.2
shows the course of the temperature during the patenting process.
In recent times, the patenting process has partly been replaced by cooling in
several stages while drawing or rolling the rod, Marcol (
1986
).
By patenting, the steel rod gets a sorbite structure (fine stripes of cementite and
ferrite) which is very suitable for drawing. In the following drawing process, the
wire cross-section is reduced in stages, for example in seven stages from 6 to
2 mm in diameter. After the wires have been patented, they can be drawn again.
The quality of the wire surface can be improved by draw-peeling the wire rod,
Kieselstein and Wißuwa (
2005
).
The principle of the wire drawing was described at an early date by Siebel
(
1959
). The strength increases with the growing decrease of the cross-section by
drawing and at the same time the breaking extension also decreases. The higher the
carbon content of the wires, the stronger they are. For wires with small diameters
below 0.8 mm, the strength can reach about 4,000 N/mm
2
, for thicker wires about
2,500 N/mm
2
, and in all cases the remaining ductility is low. The standardised
nominal strengths of rope wires are
Fig. 1.2 The course of the
temperature in the patenting
process
1100
850
°
C
quenching
lead-bath
600
400
time
Search WWH ::

Custom Search