Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
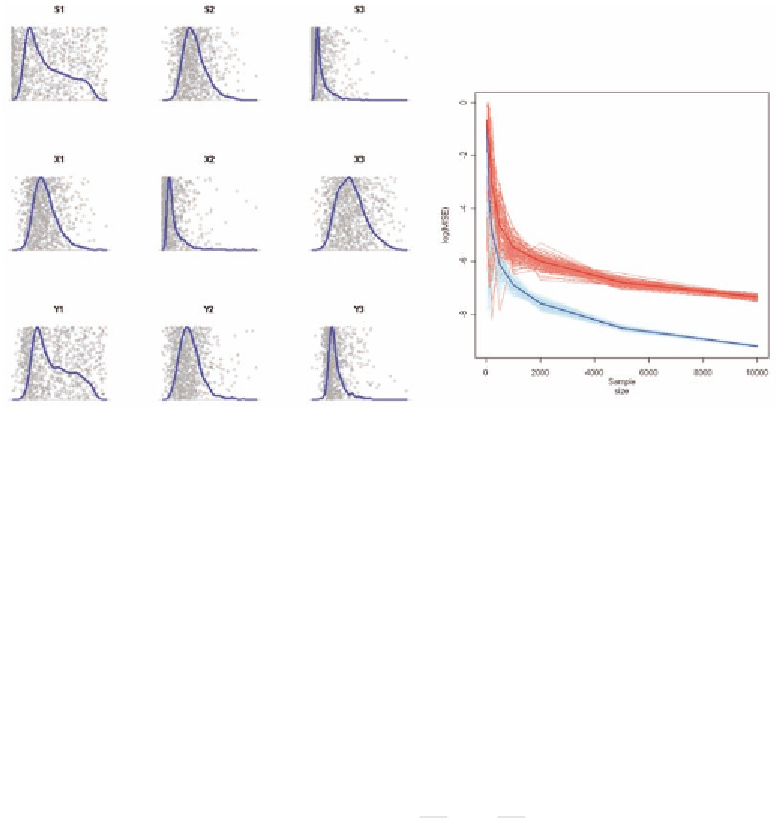
Figure 3. Left Hand Panel: CICA model applied to Gumbel-Hougard dependency gradient; Right Hand
Panel: Log Mean Integrated Squared Error (MISE) of typical ICA (fastICA) and CICA models
∂
( ( ))
G
A
y
=
∂
∂
in the model
Y
=
B
by minimizing the KL
distance (i.e. maximizing the likelihood).
Under fixed assumptions about the distribution
of the sources, two terms are minimized: the true
objective, the mutual information, expressed via
the copula; the mismatch of the marginal distribu-
tions to the assumed distributions.
Write the independence term as
X
H
*
(
−
(
G
( ),
y y
G
( )))
(13)
K
∂
A
This is the same as maximizing the
score
,
equation (14)
∂
∂
L
B
= −
∂
∂
K
( (·), ˆ(·,
q
q B
))
(14)
B
min
MI y
( ;
B
) min
=
E
(
log dC
(
( )))
u
via the marginal distributions
B
B
Θ
(11)
∂
∂
L
B
= −
∂
∂
·
and the marginal fit term as
K
(
u, u
(15)
)
B
k
∏
1
min [
C
( )
u
−
( )].
u
(12)
using the copula model. The estimates for
B
are
yielded by partial derivatives, or score maximiza-
tion ∂
Θ
i
i
=
L
/ --- either through gradient descent
or analytically. See Figure 3.
The first row are the source distributions, all
non-normally distributed:
S
∂
That is, minimize the mutual information via
the copula via rotation
B
=
ˆ
1
after minimizing
the distance between parametric copula and in-
dependent marginals. Since
A
is invertible, the
KL divergence is invariant; maximization of the
model likelihood - under independence - is
equivalent to minimizing equation (13), below.
2
~ ( (
U
−
1 1
, ))
,
1
( , )
,
S
3
2
~ χ . The second row are
the `data' observed after a full rank rotation. The
third row are the outputs - estimated sources. The
S
~
Gumbel
0 1
2