Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
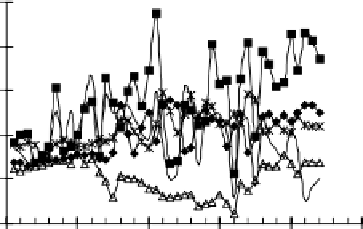
Yield (kg/ha)
3500
Ethiopia
Kenya
2800
Mozambique
2100
South Africa
1400
Zimbabwe
700
0
1960
1970
1980
1990
2000
2010
Year
Figure 6.
Development of maize yields, in selected African countries: 1961-2004
impacts in the future, by achieving gains in resource use efficiency, through man-
agement and policy interventions.
INPUT REQUIREMENTS, RESOURCE USE EFFICIENCY
AND ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Increasing competition for scarce natural resources between agriculture and other
use(r)s is a strong incentive for targeting further increases in resource use efficiencies,
in particular for nutrients and water. This, basically, applies to both, East and South-
east Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. However, significant differences exist in the type
and magnitude of the resource use problems. In Asia, in addition to the economic
aspects of reducing costs and increasing yields (for instance through better synchro-
nization of crop nutrient demand and supply), an important incentive for stimulating
improved nutrient management is reducing pollution through non-productive
nutrient emissions to water and air, resulting from excessive fertilizer use. In Sub-
Saharan Africa, on the other hand, the incentive for improving nutrient management
is rather to stop nutrient mining and/or replenish depleted soils, and enhance soil
fertility status to enable a reasonable crop cover and yield, and make the most
efficient use of precious scarce inorganic and/or organic fertilizers (Heerink 2004).
Input requirements and environmental impacts under current conditions
Yield increases in the past were heavily linked to availability and application of
man-made nitrogen fertilizer (Goudriaan et al. 2001; Frink et al. 2001; Mosier et al.
2004). Man's interventions in the global N-cycle are much more dramatic than in the
C-cycle (where just 10% is anthropogenic). Currently, at global scale, more than 85
Tg of nitrogen originate from fertilizer application (of which almost 24% is being
applied in China). Out of the 20 Tg of nitrogen fertilizer annually applied in China,

Search WWH ::

Custom Search