Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
environment
agent A
agent B
v
m
A
m
B
S
?
A
I
X
S
B
(m
A
)'
(m
B
)'
v
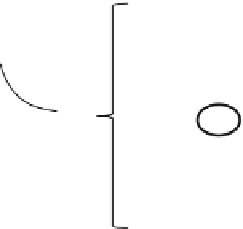
Fig. 3.11
Schema illustrating the process of agent's learning through the imitation of another
agent's activity
•
Agiven agent observes an event (e.g., an event caused by realizing a certain strategy
by a different agent), i.e. changes in the environment that make us move from the
environment
v
.
v
to the environment
v
, the agent builds the models
m
A
•
On the basis of the environments
v
and
m
A
)
, which correspond to them.
and
(
•
Afterwards, with the use of the appropriate procedure of learning through imitation
it tries to choose strategies (one or a few) so that it can be used to transfer the model
m
A
m
A
)
.
(
into
The strategy
s
?
that was found (or constructed) is memorized and completes a
given process of learning through imitation. Afterwards, this strategy may be used
by a given agent in further actions.
•
The above scenario of a learning process through the imitation of other agents'
behaviour gives possibilities of disseminating skills and experience between the
agents in the multi-agent system.
3.6.3 The Concept of the State Memorized by an Agent
As a result of the above considerations, activities performed by the agent concentrate
on choosing the appropriate strategy and realizing it in the environment.
These considerations carried out by the agent have also influence on the
information memorized by the agent. In other words, the modification of the in-
formation
M
remembered by the agent and used for the construction of the model
of a surrounding environment takes place. This modification consists in changing
stored information represented by
M
into the new
M
complemented with the expe-
rience gained. It is realized by the operation
remembering R
(Fig.
3.12
), and may be
described as follows:
M
=
R
(
M
,
m
,
s
)
(3.8)