Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
5.4.2 Operations Applied to the Evolution Agent Systems
The operations known from the classic approach to the evolution algorithms have
been enriched with new operations influencing the evolution process, which include
the aggregate operation and the migration operation (or escape).
Aggregation
is one of the operations extremely characteristic of the agent systems.
The mechanism of its operation may be presented with the use of the following
example (Fig.
5.21
):
There are four agents in the environment:
A
g
a
,
A
g
b
,
A
g
c
,
A
g
d
. Each of them is
able to change the environment in its immediate neighbourhood in the way that
it would have features desired by a given agent. It is a certain local environment
created and then kept by the agent (e.g. the agent
A
g
a
creates the local environment
E
a
,Fig.
5.21
a).
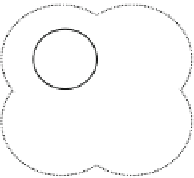
The agents may relocate in the environment, and therefore approach each other,
and consequently make their local environments overlap. In effect, the new, resul-
tant environment is established which inherits features from both (or more) local
overlapping environments.
If the environment with common features composed of the chosen features
of individual agents is established, then they may prove advantageous for the
agents (more advantageous than the environments of particular agents). Then a
group of agents is built, which undergoes consolidation. Further specialization
within the group enhances the advantageous features of the common environment
(Fig.
5.21
b).
(a)
Ag
a
E
a
Ag
d
Ag
b
E
b
Ag
c
E
c
E
d
(b)
(c)
Ag
a
Ag
b
Ag
a
Ag
b
Ag
c
Ag
d
Ag
c
Ag
d
E
x
Fig. 5.21
Schema illustrating the process of aggregation in the evolution,
a
agents in the environ-
ment,
b
a group of agents is built, which undergoes consolidation,
c
a new entity (agent) is created
as a result of the evolution process