Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
of energy, not only in primary production of commodities, but also in food
processing and distribution of agricultural products. Second, the
agricultural sector substantially contributes to energy supply, in particular
through the production of biomass, including fire wood, agricultural by-
products, animal waste, charcoal, other derived fuels and, increasingly
through production of energy crops. The share of biomass in energy
consumption differs widely for various regions in the world, ranging from
1% in Oceania, to 47% in Asia (see Figure 1.3). The share of biomass in
energy consumption depends on economic structure, the level of income,
the availability of land and other energy sources. Most of this consumption
is in the form of low efficiency conversion systems with adverse effects on
human health and the environment.
Although land is a scarce production factor in Western Europe, it is
more widely available in Eastern Europe, the USA and many developing
countries. This offers substantial scope for an increase in the production of
biomass at relatively low costs. Less productive agricultural areas and land
in set aside programmes could contribute to the production of biomass in
the USA and some countries of the EU. In many rural areas in developing
countries, bioenergy
production
is
already an
important
agricultural
activity.
Traditional use of biomass may lead to deforestation and excessive
use of natural resources. On the other hand, technological progress is
expected to bring more efficient biomass energy production systems and
enables new applications such as the production of energy from waste and
by products of agriculture.
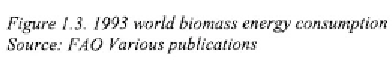

Search WWH ::

Custom Search