Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
scale is used in the analysis. Details about derivation of the input demand
equation using Shephard's lemma are omitted. The derived demand
equation for variable input
with fixed inputs
is, in intensity form:
with exogenous coefficients defined being a price index,
with symmetry constraints and linear homogeneity in prices
In this chapter is the mean share of input
i
in variable cost.
Curvature is imposed on the matrix
B
of coefficients, by the
procedure in Wiley
et al.
(1973), forming a matrix
B
=
-AA
', with a lower
triangular matrix
A
and transpose
A
'. With this reparameterisation the
estimated Hessian is negative semi-definite globally without further
restricting substitution possibilities.
Variations in energy intensity are studied. The estimated energy
intensity is decomposed in price (substitution) effect:
separate fixed inputs [capital
labor
and land
effects:
and trend effect:
The actual energy intensity is the sum of the above effects plus the
constant term, which is irrelevant in the analysis of intensity variations, and
a statistical error.
The next step is the aggregation of intensities in order to capture
the general evolution in EU agriculture. This exercise is interesting because
there is an increasing trend towards considering the EU as a whole. Even in
the case of different production structures for the different countries, a


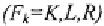
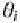

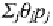

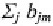
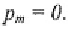

Search WWH ::

Custom Search