Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
tonnes of C per ha in wood biomass, but this ignores other biomass and soil
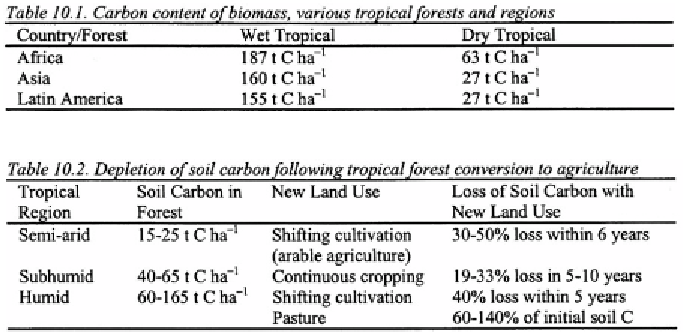
C. An indication of total C stored in biomass for various tropical forest
types and regions is provided in Table 10.1. The C sink function of soils in
tropical regions is even more variable across tropical ecosystems (see
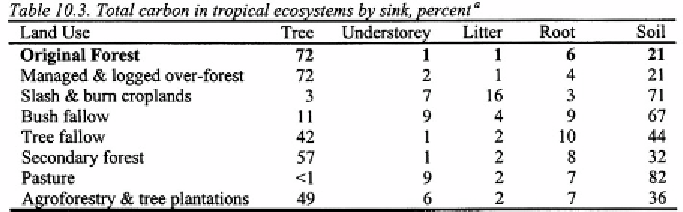
Table 10.2, col. 2). This makes it difficult to make broad statements about
carbon loss resulting from tropical deforestation. Certainly, there is a loss
in C stored in biomass (which varies from 27 to 187 t C There may
or may not be a significant loss in soil C depending on the new land use
(agricultural activity) and the tropical zone. While conversion of forests to
arable agriculture will lead to a loss of some 20-50% of soil C within 10
years, conversion to pasture may in fact increase soil C, at least in the
humid tropics (see Table 10.2). One thing is clear, conversion of forestland
to agriculture leads to a smaller carbon sink, with a greater proportion of
the ecosystem's C stored in soils as opposed to biomass (Table 10.3). To
address this market failure (release of C through deforestation), policies
need to focus on protection of tropical forests.
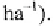
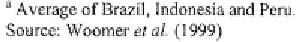
Search WWH ::

Custom Search