Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
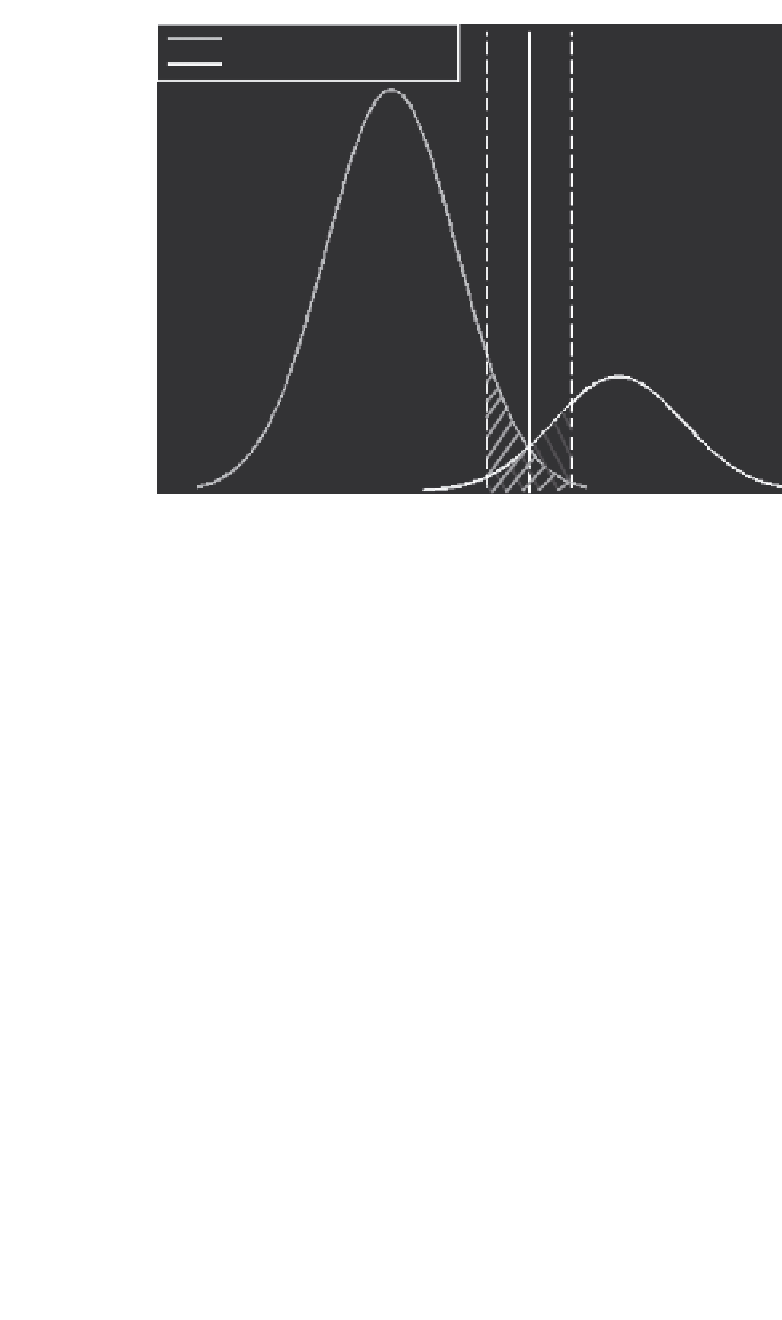
Majority samples distribution
Minority class distribution
Figure 6.3
Data within the margin is less imbalanced than the entire data.
The strategy of selecting examples within the margin also strongly addresses
the problems that arise from imbalanced classes. Consider the class distributions
of an imbalanced dataset presented in Figure 6.3. The shaded region corresponds
to the class distribution of the data within the margin. As shown in the figure,
the imbalance ratio of the classes within the margin is much smaller than the
class imbalance ratio of the entire dataset. Therefore, any selection strategy that
focuses on the examples in the margin most likely ends up with a more balanced
class distribution than that of the entire dataset.
Throughout this section, the discussion is constrained to standard two-class
classification problems using SVMs. The next section presents a brief overview
of SVMs, followed by the working principles of an efficient AL algorithm in
Section 6.3.2. We explain the advantage of using online SVMs with the active
sample selection in Section 6.3.3.
6.3.1 Support Vector Machines
SVMs [26] are well known for their strong theoretical foundations, generalization
performance, and ability to handle high dimensional data. In the binary classifi-
cation setting, let
((x
1
,y
1
)
···
(x
n
,y
n
))
be the training dataset, where
x
i
are the
feature vectors representing the instances and
y
i
∈
(
−
1
,
+
1
)
be the labels of the
instances. Using the training set, SVM builds an optimum hyperplane—a lin-
ear discriminant in a higher dimensional feature space—that separates the two








Search WWH ::

Custom Search