Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
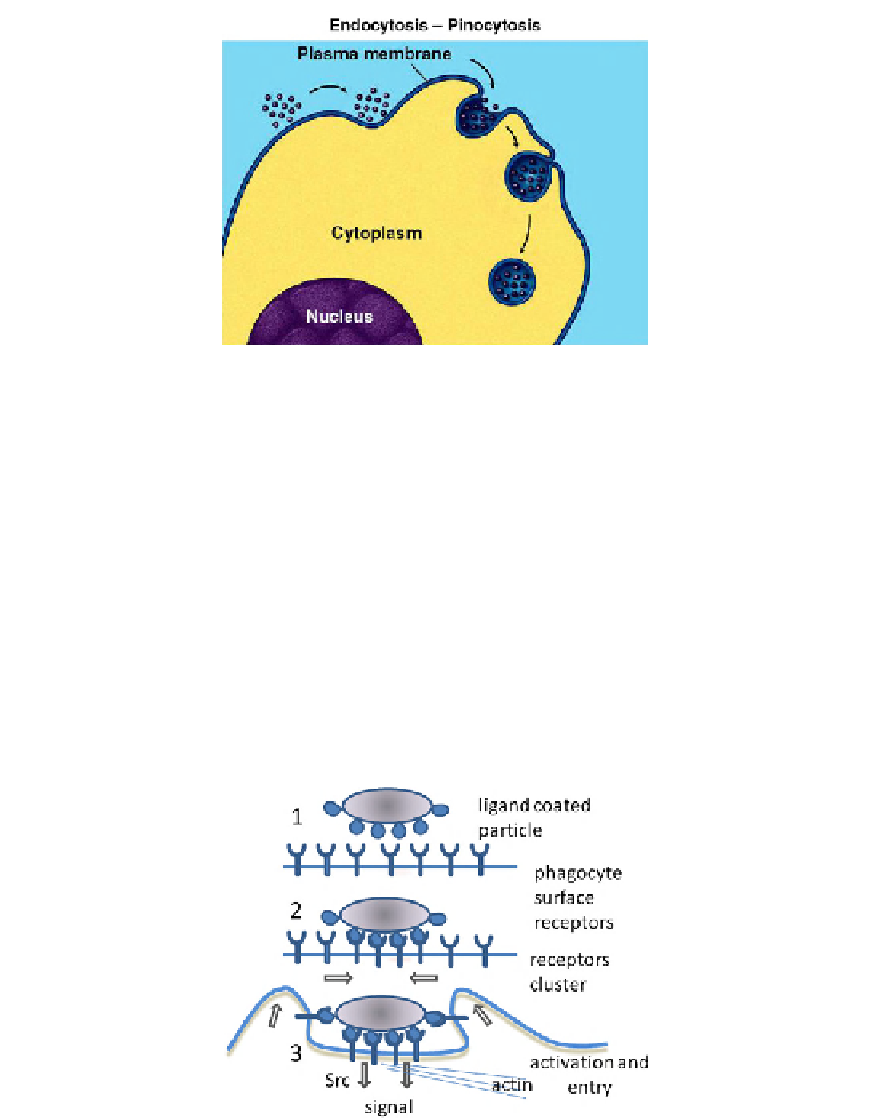
FIGURE 14.24
Pinocytosis, a type of endocytosis. An invagination of the plasma membrane encapsulates many
water-soluble solutes ranging in size from salts to macromolecules. Courtesy of Dr. Gary Kaiser
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis that involves uptake of large solid particles, often
>
m
[53]
. The particles are aggregates of macromolecules, parts of other cells and even
whole microorganisms and, in contrast to pinocytosis, phagocytosis (shown in
Figure 14.25
)
has surface proteins that specifically recognize and bind to the solid particles.
Figure 14.25
[54]
depicts events in phagocytosis. Phagocytosis is a routine process that amoeba and cili-
ated protozoa use to obtain food. In humans phagocytosis is restricted to specialized cells
called phagocytes that include white blood cell neutrophils and macrophages. As with
pinocytosis, phagocytosis generates intracellular vesicles called phagosomes that have
sequestered solid particles they transport to the lysosome for digestion. Phagocytosis is
0.5
m
FIGURE 14.25
Phagocytosis, a type of endocytosis that involves uptake of large solid particles
[65]
.