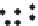Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
phospholipid, the process is complete in approximately one to two minutes. The process is
much slower with poorly hydrated lipids such as PE and with phospholipids containing
long saturated chains with high T
m
s. Liposome versatility makes them important for
many types of scientific investigations. Liposomes can sequester water-soluble solutes in
their aqueous interiors and house membrane integral proteins in their bilayers. Since lipo-
somes can also be made from non-immunogenic membrane lipids, they have obvious poten-
tial as drug delivery vehicles (see Chapter 15), and indeed thousands of examples of such
vehicles can be found in the medical literature
[39,40]
. Besides the very simple method for
making multilamellar liposomes described above, there are a wide variety of alternate meth-
odologies used in the production of other types of liposomes. Before we proceed to some of
these methodologies, a brief description of size exclusion chromatography (also known for
life science applications as gel filtration chromatography) is appropriate.
One important use for liposomes is in measuring trans-membrane solute diffusion. Since
lipid bilayers are poorly permeable to most solutes, solute gradients can be readily estab-
lished across the liposomal membranes. One important way to create solute gradients is
by use of size exclusion (gel filtration) chromatography, a process that allows rapid separa-
tion of big from small particles (
Figure 13.15
). The technique was first described in the mid
1950s by Lathe and Ruthven
[41,42]
and requires at least a 10% difference in size between the
two particles. This criterion is easily met when very large liposomes are separated from very
small solutes
[43]
. The most commonly used stationary phase for gel filtration is the resin
Sephadex
. Sephadex is a trademark for cross-linked dextran gels made by Pharmacia since
1959. Sephadex comes in several discrete bead sizes (Sephadex G-10, G-15, G-25, G-50, G-75,
and G-100) with properties altered by the extent of cross-linking. The stationary phase is
: Small molecule
: Large molecule
FIGURE 13.15
Separation of small from big particles using gel filtration (size exclusion) chromatography
[81]
.