Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Docosahexaenoic Acid Structure
MD Configurations
Stick
Bent Stick
·
o
o
·
o
o
General Shape
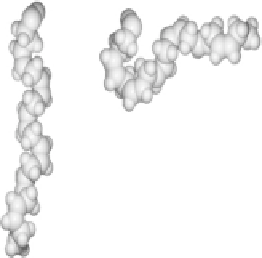
FIGURE 10.21
Several views of the structure of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
[59]
.
conformers of the many possibilities, as determined by molecular dynamics (MD) simula-
tions, are shown in
Figure 10.21 [59]
. The average of all conformations makes DHA
a cone-shaped molecule (
Figure 10.21
) that, when incorporated into phospholipids, would
prefer being in a non-lamellar phase. DHA-phospholipids are loosely packed and can induce
negative curvature strain to its immediate membrane neighborhood. These concepts will be
discussed in detail below. Combined MD simulations of rhodopsin and DHA by Scott Feller
of Wabash College have resulted in a startling observation. DHA finds and fits perfectly into
a groove on rhodopsin's surface (
Figure 10.22
)
[60]
! This, of course, suggests the existence of
FIGURE 10.22
Molecular dynamics simulation of rhodopsin (blue) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, white).
DHA fits into a groove on the surface of rhodopsin
[60]
.