Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
300
Main Transition
250
200
GEL
LIQUID
CRYSTAL
150
100
Pre-Transition
50
0
-50
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Temperature (˚C)
GEL
L
β'
LIQUID CRYSTAL
L
α
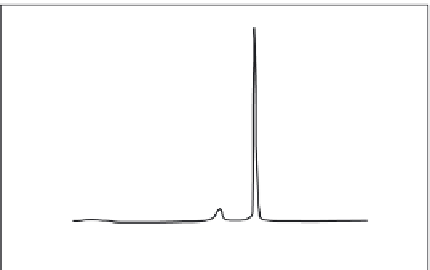
FIGURE 9.22
DSC scan of the gel (L
b
'
) to liquid crystal (L
a
) transition for DPPC. For disaturated chain PCs in
the gel state, the chains are tilted in relation to the polar head group. Upon melting to the liquid crystal state, the tilt
disappears.
Due to the lack of 'gauche kinks', saturated acyl chains below their melting point pack
tightly while the same chains above their melting point pack loosely (
Figure 9.22
). Lipid
packing as related to melting affects several important, basic membrane properties.
Compared to gel-state membranes, liquid crystalline state membranes:
1.
Are more poorly packed.
2.
Occupy a larger area per lipid.
3.
Are more fluid.
4.
Are more permeable.
5.
Are thinner.
6.
Are less stable.
7.
Are more dynamic.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
The most direct method for monitoring melting in lipid bilayers is by differential scanning
calorimetry (DSC). The technique was developed by E.S. Watson and M.J. O'Neill in 1960 and
was rapidly moved into commercial production by 1963. DSC is a non-perturbing, analytical